Bone Structure and Ossification chapter wise MBBS basic science MCQ CEE Nepal
Bone Structure and Ossification
The human skeleton is composed of 206 bones that provide structure, support, and protection to the body. Bones can be classified based on their shape and function. The main types of bones include:
Types of Bones
- Long Bones: Characterized by a long shaft and are primarily responsible for weight support and movement. Examples include the femur and humerus.
- Short Bones: Cube-shaped and provide stability with little movement, such as the carpals and tarsals.
- Flat Bones: Provide protection to internal organs and serve as attachment sites for muscles, such as the skull and sternum.
- Irregular Bones: Complex shapes that do not fit into other categories, like vertebrae.
- Sesamoid Bones: Develop within tendons and help protect joints, with the patella being the most notable example.
Parts of Bone
Each bone consists of several key components:
- Diaphysis: The long central shaft of a long bone.
- Epiphysis: The end part of a long bone, which contains red marrow and is covered by articular cartilage.
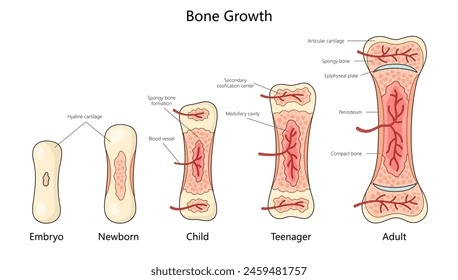
- Metaphysis: The region between the diaphysis and epiphysis, where growth occurs in children.
- Medullary Cavity: The hollow space within the diaphysis that contains yellow bone marrow.
- Periosteum: A dense layer of vascular connective tissue that envelops the bones except at the surfaces of the joints.
Ossification
Ossification is the process of bone formation, which can occur through two primary mechanisms:
- Intramembranous Ossification: This process occurs when bone develops directly from mesenchymal tissue, forming flat bones like the skull.
- Endochondral Ossification: This process involves the replacement of hyaline cartilage with bone, which is typical in the development of long bones.
Bone growth continues throughout childhood and adolescence, facilitated by the epiphyseal plates, which close after puberty, leading to the cessation of growth in length. Understanding the structure and function of bones is crucial for medical students, as it lays the foundation for comprehending human anatomy and pathology.

 Posted by
Posted by 
No comments: